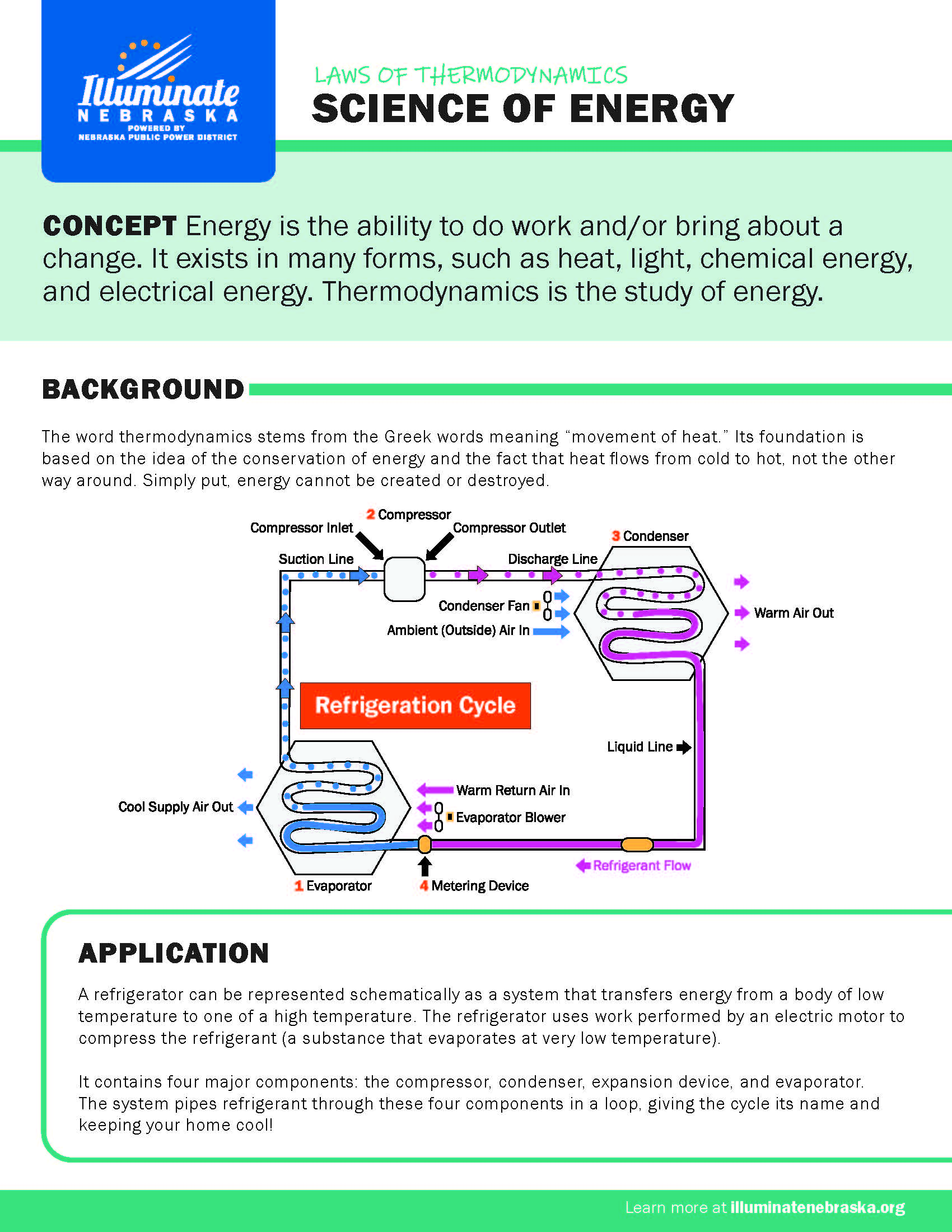
Science of Energy
Energy is the ability to do work and/or bring about a change. It exists in many forms, such as heat, light, chemical energy, and electrical energy. Thermodynamics is the study of energy.
Fundamentals of Efficiency
In this lesson on the laws of thermodynamics and fundamentals of efficiency, students will learn the basic principles governing energy transfer and conversion. The lesson will begin with an introduction to the three laws of thermodynamics, including the conservation of energy, the tendency of energy to move from high to low concentrations, and the impossibility of achieving absolute zero temperature.
Connected to Kirkoff’s Law
Students will learn about the basic principles of thermodynamics, including the first and second laws, and how they relate to electrical circuits. They will also learn about Kirchhoff’s laws, which describe the behavior of electric circuits, and how these laws are connected to the laws of thermodynamics.
Heat Engine
Heat engines are mechanical systems that convert thermal energy into mechanical work, operating based on the principles of the Laws of Thermodynamics. The first law, also known as the conservation of energy, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another.
Entropy
Entropy is a measure of the disorder of a system. Entropy also describes how much energy is not available to do work. The more disordered a system and higher the entropy, the less of a system’s energy is available to do work.