Materials
The selection of materials in robotics depends on factors such as the robot’s size, weight, power requirements, operating environment, and desired performance criteria. Common materials include metals such as aluminum and steel for structural components and sensors, plastics for lightweight parts, and composites for high-strength and durability. Soft materials such as silicone and rubber are also increasingly being used.
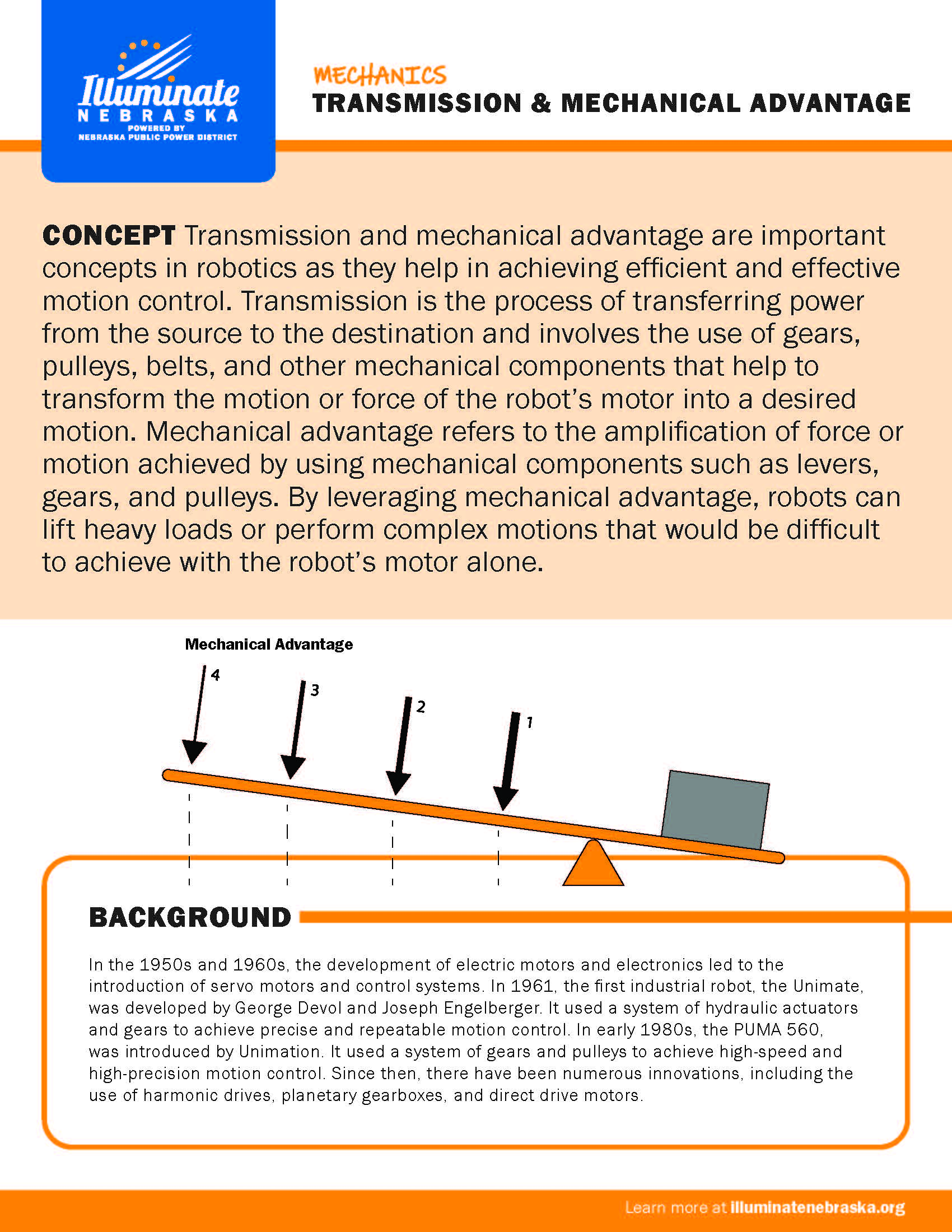
Transmission & Mechanical Advantage
Transmission and mechanical advantage are important concepts in robotics as they help in achieving efficient and effective motion control. Transmission is the process of transferring power from the source to the destination and involves the use of gears, pulleys, belts, and other mechanical components that help to transform the motion or force of the robot’s motor into a desired motion.
Fabrication Foundations
Fabrication foundations are the fundamental concepts, materials, and processes used to design, manufacture, and assemble robotic systems. This includes a range of techniques such as computer-aided design (CAD), 3D printing, laser cutting, welding, and assembly methods. The goal of fabrication is to create robotic systems that are efficient, precise, and reliable, and can perform complex tasks in various applications such as manufacturing, healthcare, and exploration.
Drive Trains
In robotics, a drive train is the mechanism that propels the robot. It usually consists of a motor, wheels or tracks, and a controller that manages the movement of the robot. The type of drive train used in a robot will depend on the specific application, such as speed, maneuverability, or terrain.
Mechanical Design Basics
The design phase of a project is when all the important questions get asked and answered. Ask yourself: How should this part look, what will it be used for, and what should it do? This is where the creativity meets planning, so your project goes in the right direction.