PWM | Motor Control
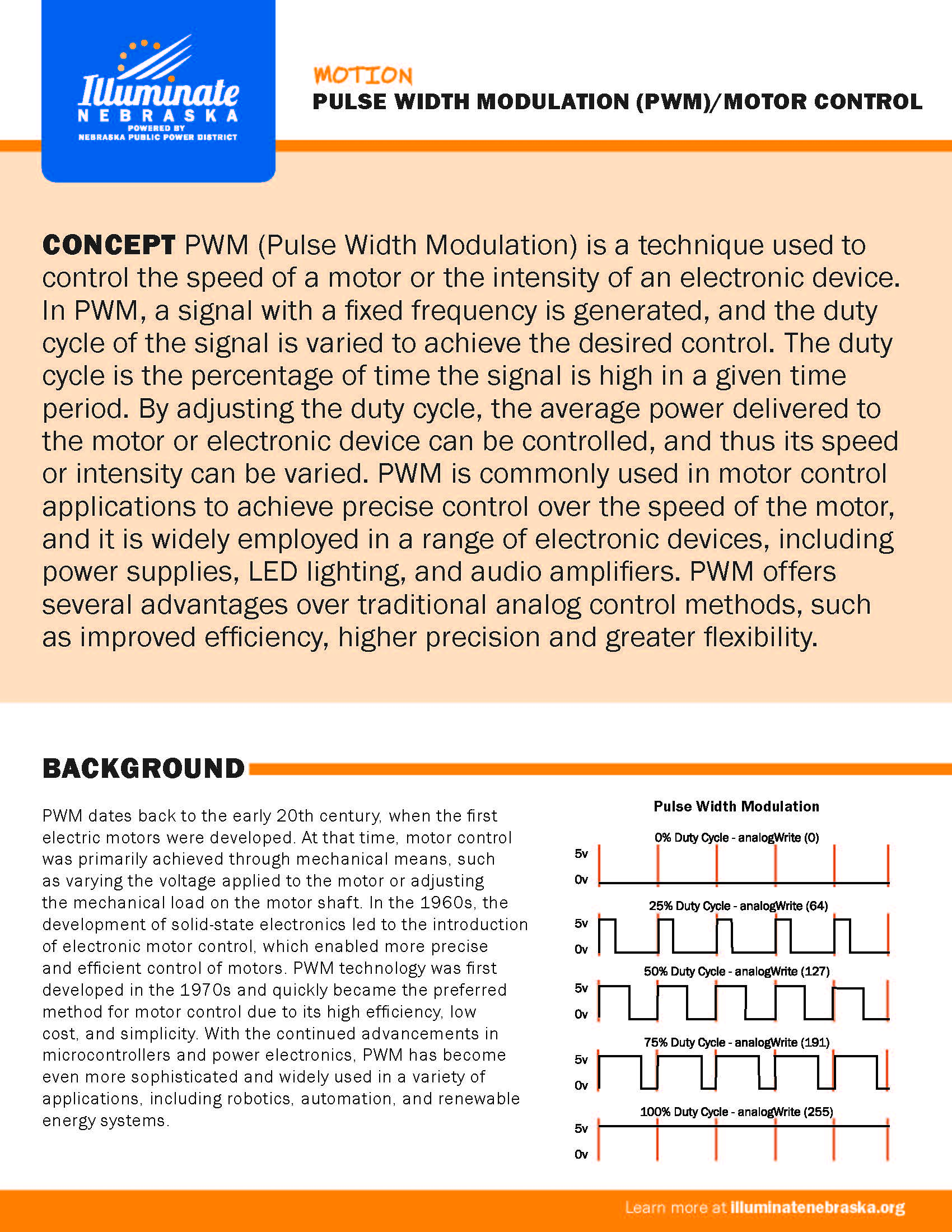
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is a technique used to control the speed of a motor or the intensity of an electronic device. In PWM, a signal with a fixed frequency is generated, and the duty cycle of the signal is varied to achieve the desired control. The duty cycle is the percentage of time the signal is high in a given time period.
Types of Motors
There are several types of motors commonly used in robotics, including DC motors, servo motors, stepper motors, AC motors, hydraulic motors, and pneumatic motors. DC motors are simple to control and can be used for a wide range of applications. Servo motors are designed for precise positioning and are commonly used in robotic arms.
Measuring Motion
Measuring motion is critical in robotics for accurate positioning, precise movement control, safety, and efficiency. Accurate measurement enables robots to navigate, interact, and perform their tasks effectively, while optimizing energy consumption and reducing costs.
Control Loops
Control loops enable robots to continuously monitor and adjust their movements in realtime, ensuring that they reach their intended target with the required speed, position, and orientation. By using sensors to detect the robot’s current state, such as its position, velocity, and acceleration, control loops can make accurate predictions about the robot’s future state and adjust its movements accordingly.
Power | RPM | Torque | Watts | KV
Coming Soon!