Sine / Cosine / Tangents
The trigonometric functions are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of the two side lengths that form the right angle and the length of the hypotenuse opposite the right angle itself. These ratios are widely used in all sciences, industry, and engineering applications related to geometry and perpendicular lines within the various X, Y and Z planes.
Torque / Displacement
In trigonometry, torque and displacement are related to the concept of circular motion. Torque is the measure of the force that causes an object to rotate around an axis or pivot point, while displacement is the distance and direction that an object has moved from its initial position.
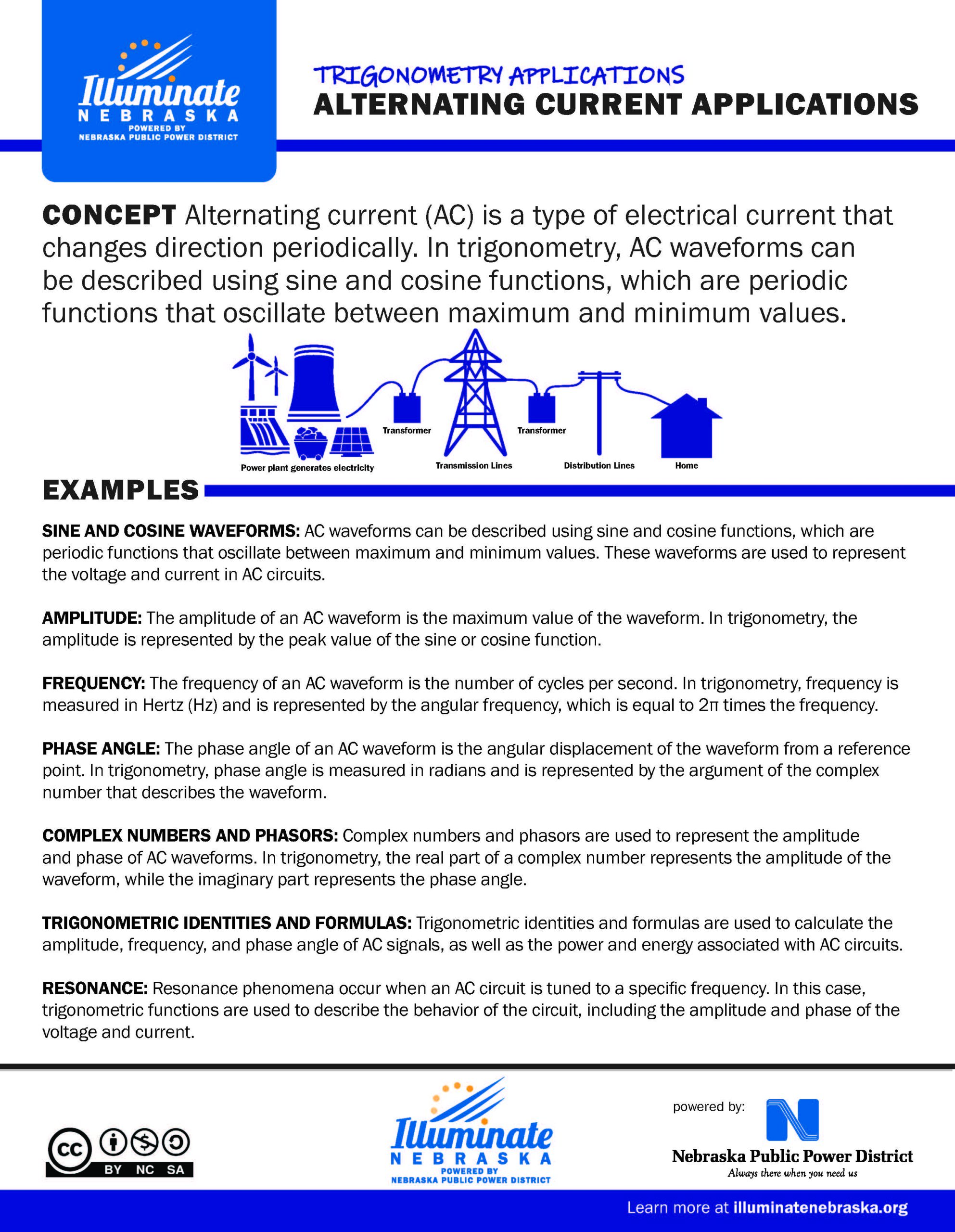
Alternating Current Applications
Alternating current (AC) is a type of electrical current that changes direction periodically. In trigonometry, AC waveforms can be described using sine and cosine functions, which are periodic functions that oscillate between maximum and minimum values.
Unit Circle
In trigonometry, the unit circle is a circle with a radius of one unit, centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. It is commonly used to define the values of the six trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent) for any angle in radians or degrees. The unit circle is divided into four quadrants, each containing angles with positive or negative values of sine, cosine, and tangent.
Kinematic Analysis
Kinematic analysis is the process of using trigonometric functions and equations to study the motion of objects. It involves analyzing the position, velocity, and acceleration of an object in motion, as well as the forces acting upon it. Kinematic analysis is used in a variety of fields, including physics, engineering, and astronomy, to study and predict the motion of objects in space and time.