Controlling Speed & Direction
Controlling the speed and direction of electric motors is important to many applications of electricity. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) has been used to control the speed and direction of electric motors.
Waves
A disturbance that transfers energy.
Proportional / Integral / Derivative
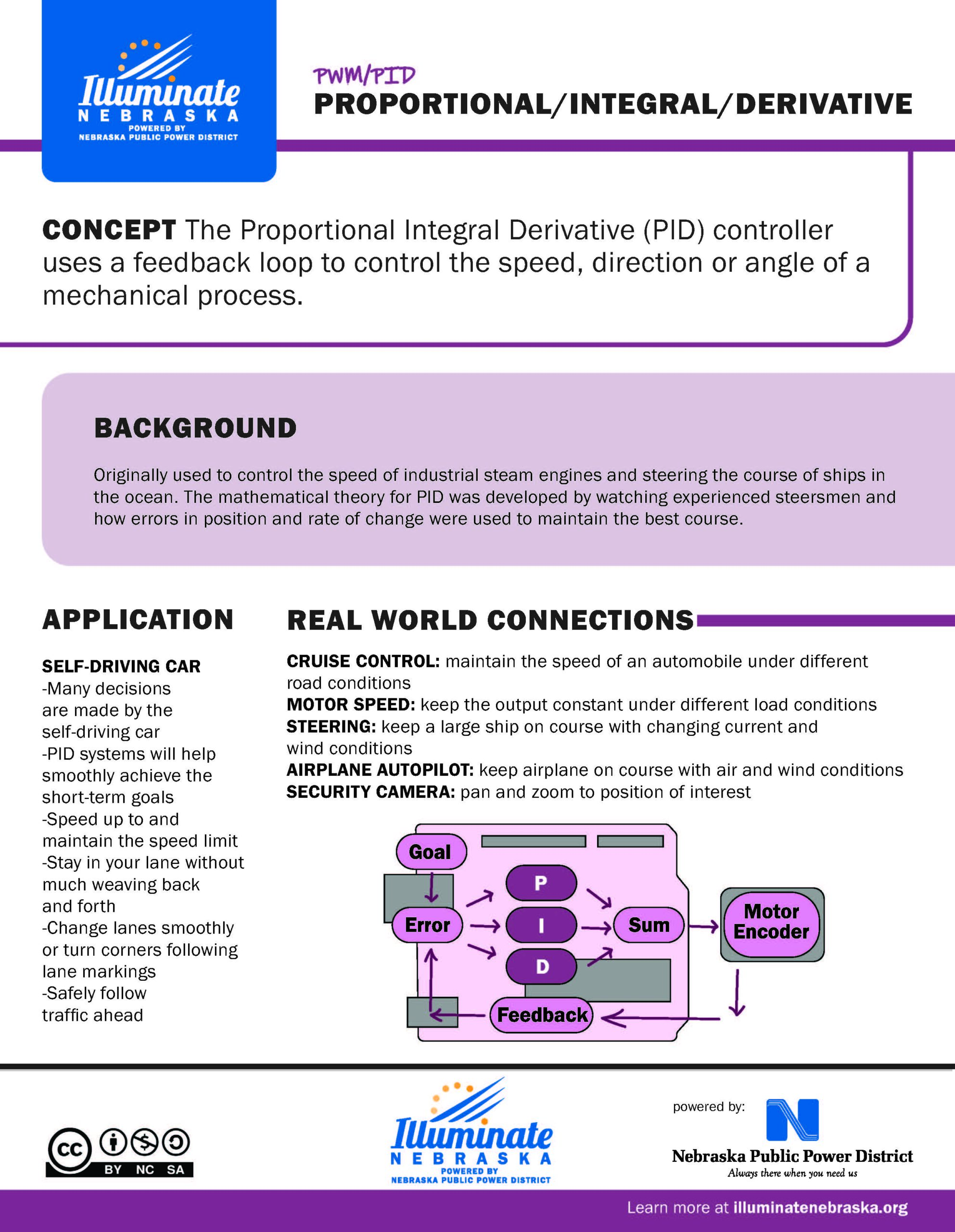
The Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller uses a feedback loop to control the speed, direction or angle of a mechanical process.
Motor Controllers
Motor controllers are electronic devices that regulate the speed, direction, and torque of electric motors. They are widely used in industrial applications, such as manufacturing, robotics, and automotive systems, as well as in consumer products, such as appliances and power tools. Motor controllers can be programmed to control the motor’s output based on various inputs, such as temperature, pressure, or user commands.
Variable Frequency Drive
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is an electronic device that is used to control the speed and torque of an electric motor by varying the frequency and voltage of the electrical input signal. The VFD is capable of controlling the motor at different speeds and torque levels, which makes it a versatile solution for many different applications.